Product design involves the process of creating and developing new products to enhance functionality, usability, and aesthetics. It plays a crucial role in shaping everyday objects by addressing user needs and preferences, ensuring that products are both practical and appealing. Through thoughtful design, everyday items can improve quality of life, enhance user experiences, and influence consumer behavior.
Product design seamlessly integrates functionality, aesthetics, and innovation to create effective and appealing objects. Functionality ensures that products meet user needs and perform their intended tasks efficiently.
Aesthetics enhance the visual appeal and emotional connection, making the product attractive to consumers. Innovation drives creativity and the incorporation of new technologies or ideas, resulting in unique solutions that enhance user experience and differentiate products in the market.
B.Des Program: 10+2 (Any of the State Boards/ CBSE/ ICSE/ ISC/ CIE/ IB/ NIOS or equivalent exam) from any stream.
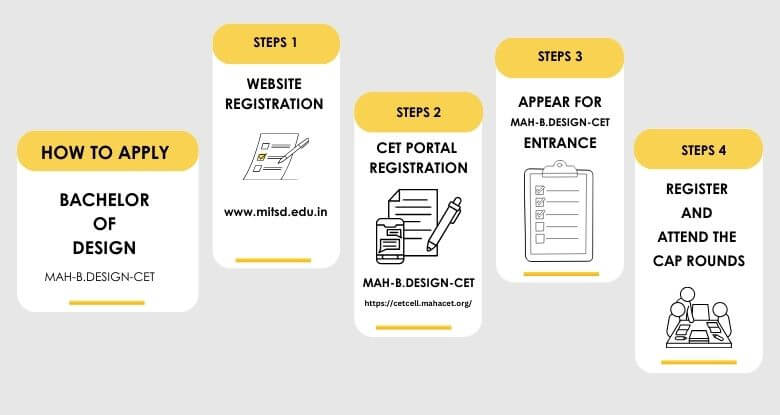
Go to the official website of MIT Institute of Design (MITSD) or MIT School of Design. Look for the Admissions section on the homepage.
Admissions only through MAH-B Design CET entrance exam.
College Code - 06146.
List of 10 Career opportunities
The Product Design program at MIT School of Design (MITSD) is mentored by Prof. Uday Athavankar, a renowned architect from J J School of Arts and former IIT Bombay professor, who brings over 50 years of expertise in design education and consulting. A trailblazer in integrating new technologies and research into design, Prof. Athavankar has been instrumental in shaping India's design education. MITSD's curriculum covers crucial areas like user-centered design, materials, manufacturing processes, and sustainability. It emphasizes hands-on learning through workshops and live projects, allowing students to apply their knowledge practically and develop strong portfolios. State-of-the-art facilities provide space for innovation, while robust industry connections offer valuable internships.
The experienced faculty at MITSD, hailing from esteemed institutions like IIT Mumbai, Delhi, Guwahati, and SPA Bhopal, bring diverse expertise to the Product Design program. Their combined focus on sustainability and innovation equips students with the knowledge and skills needed to design impactful, future-ready products. This holistic approach ensures graduates are well-prepared to tackle modern design challenges and create meaningful, forward-thinking solutions.
A career in product design requires a blend of technical and creative skills, including proficiency in design software (such as CAD and Adobe Creative Suite), strong problem-solving abilities, and an understanding of user-centered design principles. Additionally, effective communication, collaboration skills, and knowledge of materials and manufacturing processes are essential to bring innovative ideas to life and work effectively with cross-functional teams.
MIT School of Design (MITSD) approaches product design by emphasizing a user-centered design methodology that integrates research, creativity, and technical skills. The curriculum focuses on hands-on projects, fostering collaboration across disciplines, and developing an understanding of market needs and sustainability. Students engage in real-world problem-solving, enabling them to create innovative and functional products that resonate with users and meet industry standards.
Product design primarily focuses on the conceptualization and creation of individual items, considering aspects like aesthetics, functionality, and user experience. In contrast, industrial design encompasses a broader scope, involving the design of products for mass production while addressing manufacturing processes, ergonomics, and market viability. While both fields share similarities, industrial design often emphasizes the larger context of products within systems and environments.
Product design can shape the future of sustainable products by prioritizing eco-friendly materials, efficient manufacturing processes, and modular designs that promote longevity and recyclability. By integrating sustainability principles from the outset, designers can create products that minimize waste, reduce carbon footprints, and promote a circular economy. This approach not only addresses environmental challenges but also meets the growing consumer demand for responsible and sustainable solutions.
Ergonomics plays a crucial role in product design by ensuring that products are tailored to fit the users' needs, capabilities, and limitations. It focuses on enhancing user comfort, safety, and efficiency by considering factors like body dimensions, movement, and interaction. By integrating ergonomic principles, designers can create products that improve user experience, reduce the risk of injury, and increase overall satisfaction, making them more effective and appealing.
Product designers use a variety of software and tools to create, prototype, and test designs. Key tools include CAD software like SolidWorks, AutoCAD, and Fusion 360 for 3D modeling, as well as Adobe Creative Suite (Illustrator, Photoshop) for visual design. Prototyping tools such as Rhino, KeyShot for rendering, and 3D printers are also essential for developing and refining physical models. These tools help designers bring concepts to life and ensure functional, aesthetically pleasing products.
User-centered design is critical in product design as it ensures that products meet the actual needs, preferences, and behaviors of the end users. By focusing on usability, functionality, and user experience, designers can create solutions that are intuitive, accessible, and effective. This approach not only enhances customer satisfaction but also increases the product’s success in the market by addressing real-world problems.
The latest trends in product design include a strong focus on sustainability, with designers prioritizing eco-friendly materials and circular design principles. There’s also a growing emphasis on user experience (UX), personalization, and modularity, allowing products to be more adaptable and customizable. Additionally, the integration of smart technology and AI-driven design solutions is increasingly shaping products to be more connected and intelligent, enhancing functionality and user interaction.
Design thinking plays a pivotal role in product design by fostering a human-centered, iterative approach to problem-solving. It encourages designers to empathize with users, define key challenges, ideate creative solutions, prototype, and test concepts. This process promotes innovation, collaboration, and flexibility, helping designers develop products that effectively meet user needs and address real-world problems.